Collaborative what?
Taking a glance at collaborative robotics
Did you know that material handling is projected to be the biggest area of application for collaborative robots (cobots) in 2022?
Nowadays, the cobot market is booming, because this technology ensures a high-level of flexibility during manufacturing processes, economic benefits and individuals’ ergonomic advantages. But what are cobots in the first place? To develop a better understanding on what cobots are, it is important to consider the way they interact with workers.
The International Federation of Robotics distinguishes between four types of collaboration between robots and human workers:
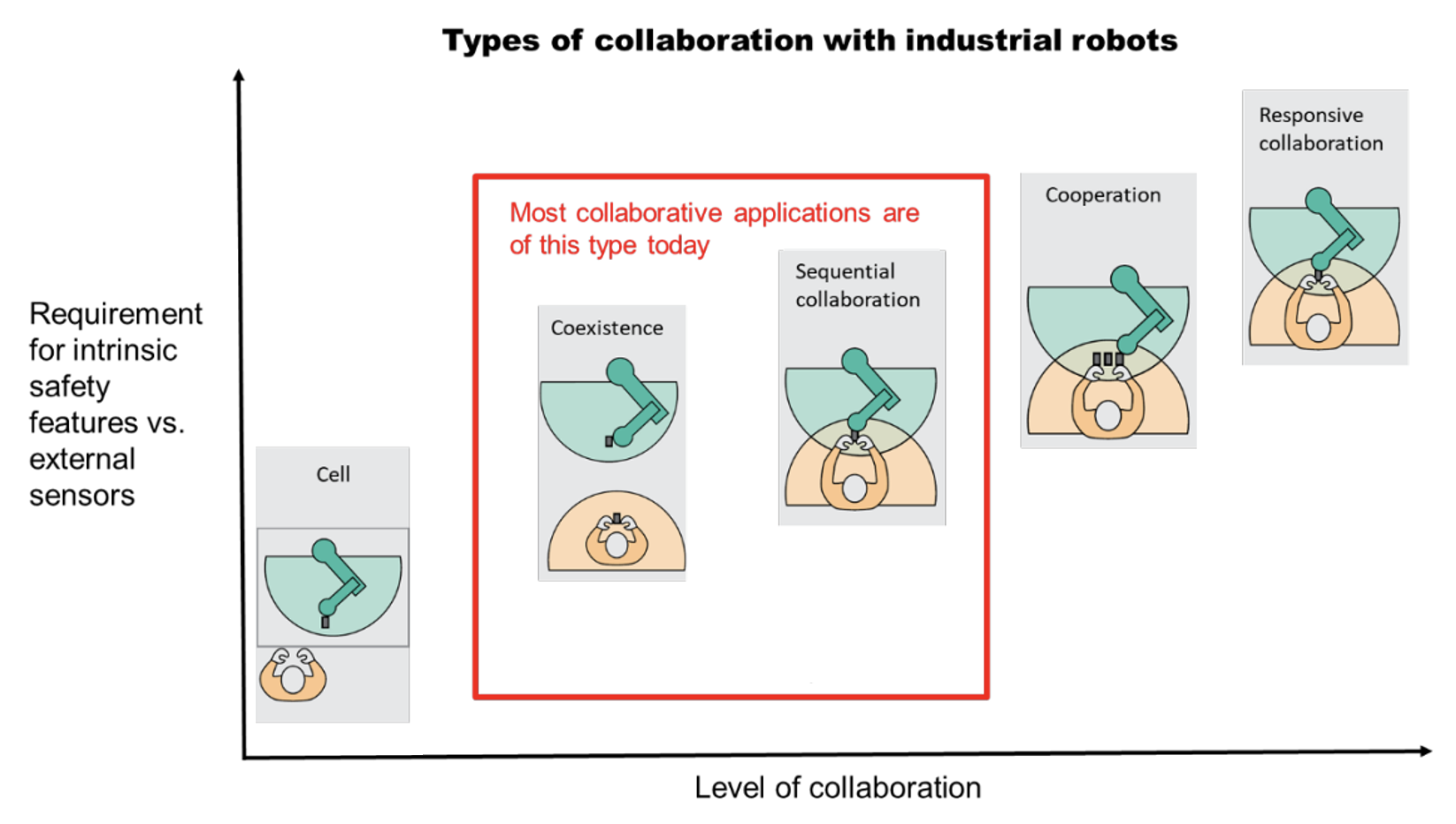
Types of collaboration with industrial robots (Source: IFA, 2018)
The interaction can be designed in a coexistent environment, in the sense that workers and robots work together without security barriers, but the workplace is not shared. This kind of interaction represents the safest type of collaboration between robots and humans. In sequential collaboration, the robot and the human worker share a workspace but the work process and movements are designed sequentially.
Furthermore, robots and human can work in motion and at the same time, which is called cooperative collaboration. Finally, responsive collaboration represents the kind of collaboration where robots respond to workers movements in real time. This type of interaction is classified as the highest level of collaboration and sets huge emphasis on requirements for robotic sensors and worker’s safety and security standards.
Nowadays, the most applicable types of collaboration are coexistence and sequential collaboration. The integration of cobots help the workers in terms of ergonomics, as the purpose of implementation is not only to increase the production efficiency but also to reduce workers’ biomechanical overload.
Conducting research
Thus, the implementation of cobots is extremely beneficial for companies that aim to improve their manufacturing processes, but also for worker’s safety.
However, the integration of this technology can be assumed as biggest challenges for companies, because of missing methodology for the analysis of workplaces. In order to detect possible workloads and fields of application, research has to be conducted. Currently I’m synthesizing and analyzing the literature in order to develop a deep understanding of the general implementation of cobots in organizations. My goal is to cluster the knowledge gained from the review and extract factors that facilitate the integration and adoption of cobots.
The journey goes on
Personally, it is an exciting and wonderful task to delve into the subject and to be guided by different perspectives and aims. It is becoming more and more apparent that technology is not just about technology alone, but much more about people. The expansion of people’s capabilities is central here.
During the last weeks we have established task forces within the EINST4INE team in order to practice and experiment some of the usual roles of a researcher including exploring matters and being empowered on project management activities. I’m happy to be part of the task forces that are responsible for technology awareness and socializing.
I’m looking forward to attend the Summer School (Spain) during July and the Robotic Conference NordiCHI (Denmark) in October. These events certainly contribute to my research as synergy drivers and it will be great to see my EINST4INE colleagues in person again.
References:
International Federation of Robotics, Demystifying Collaborative Industrial Robots, 2018. Source: https://web.archive.org/web/20190823143255/https://ifr.org/downloads/papers/IFR_Demystifying_Collaborative_Robots.pdf


Add a Comment